In medical device design, optimal usability is paramount, and a critical design principle to achieve this goal is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Originating from Tanner & Swets decision-making theory of visual detection (1954), signal-to-noise ratio plays a vital role in enhancing the effectiveness, efficiency, and user satisfaction of medical devices. This blog post will examine the concept of SNR, its significance for medical device manufacturers, and how designers can use it to enhance usability.
What is Signal-to-Noise Ratio?
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. In the context of medical device usability, the “signal” represents the critical information or functionality that needs to be conveyed to the user, while the “noise” includes any extraneous information or distractions that could obscure or detract from the signal.
It’s crucial to recognize that what constitutes a signal or noise varies based on the user’s current goals; a signal in one context may become noise in another. For instance, consider a patient monitor displaying multiple data pieces.
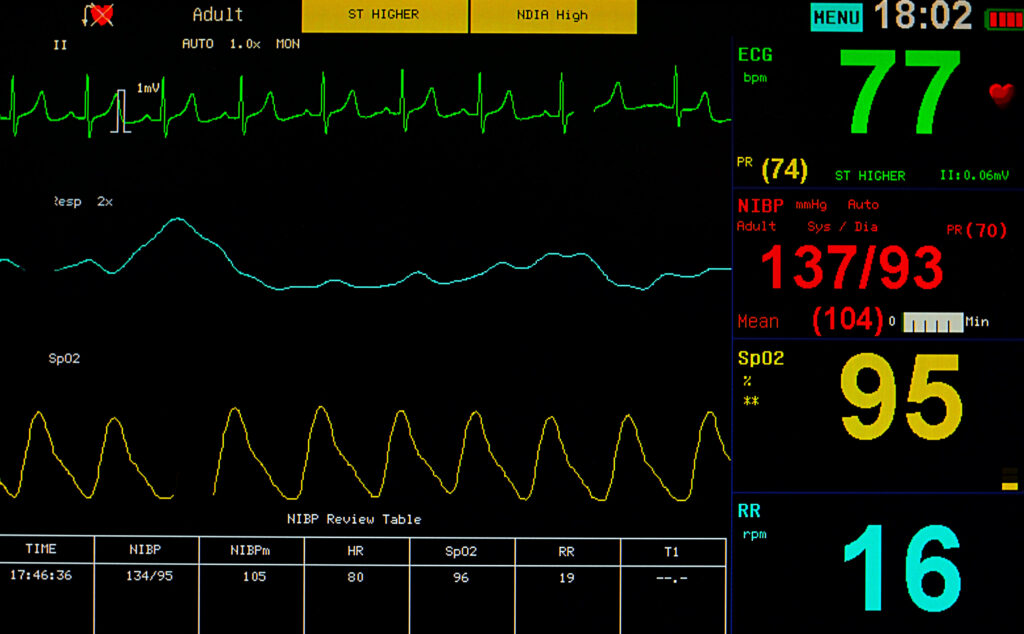
When a nurse uses a patient monitor to assess oxygen saturation (SpO2), the SpO2 value represents the signal, while everything else would be considered noise. However, if the nurse then seeks the patient’s respiratory rate, the SpO2 value transitions to noise.
A high SNR means that the important information stands out clearly against the background, making it easier for users to focus on what matters most. Conversely, a low SNR indicates that the essential information is buried under, or within, a lot of unnecessary details. Designers should strive for the highest SNR possible; low signal-to-noise ratios often lead to confusion, use errors, and therefore safety issues.
Why is Signal-to-Noise Ratio Important?
Simply put, high signal-to-noise ratios mean users can find the information they need quickly. This has several advantages:
Enhances Patient Safety: High SNRs ensure that critical information is clear and easily accessible, minimizing the likelihood of use errors. In a medical context, these errors can have severe, even fatal, consequences, so clear, unambiguous information presentation is vital for preventing them.
Additionally, when the essential data stands out prominently, healthcare professionals can make faster and more accurate decisions. This is particularly important in emergent situations where every second counts.
Improves Efficiency: Devices with a high SNR help in reducing cognitive load by filtering out unnecessary information. This allows healthcare providers to focus on the task at hand without irrelevant details distracting them, leading to a more efficient workflow.
Devices that are easy to understand and use also require less training time. Medical staff can quickly become proficient with devices that highlight key information and minimize noise.
Boosts User Satisfaction: A user-friendly device with a high SNR is more likely to be positively received by medical staff. When users can easily find and interpret the information they need, their overall experience with the device improves.
Complies with Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory bodies like the FDA emphasize human factors and usability in medical devices. High SNR aligns with these guidelines by promoting clarity and usability, which can facilitate the approval process.
How Medical Device Manufacturers Can Use the SNR Principle
Simplified Interface Design: Ensure you display the most critical information prominently. Minimize unnecessary details or remove them to avoid clutter. Reduce the number of buttons, controls, and settings to those that are absolutely necessary. This helps users focus on the most important tasks without getting overwhelmed.
Clear Visual Hierarchy: Utilize larger fonts, bold text, and contrasting colors to highlight key information. Less important information can be displayed in smaller fonts or muted colors. Organize information logically with adequate spacing. Group related elements together and separate different sections clearly to enhance readability.
Consistent and Intuitive Icons: Use industry-standard icons that are easily recognizable. This helps users quickly identify functions and information without needing to interpret new symbols. Also, ensure you use icons and symbols consistently across different devices and interfaces to prevent confusion.
Effective Use of Alerts and Alarms: Design alarm systems to prioritize critical alerts over less urgent ones. Ensure that important alarms are distinguishable through unique sounds or visual cues. Avoid excessive alarms that can desensitize users. Use context-sensitive alarms that only activate when necessary.
Minimalist Design: Remove redundant features and controls that do not contribute to the core functionality of the device. Focus on simplicity and ease of use. Include only those features that are essential for the device’s primary functions. This helps maintain a high SNR by keeping the user interface clean and focused.
Conclusion
Incorporating the signal-to-noise ratio principle into medical device design is crucial for enhancing usability. By focusing on presenting critical information clearly and minimizing distractions, manufacturers can create devices that are safer, more efficient, and more satisfying to use. As the medical field continues to evolve, the importance of high SNR in device design will only grow, underscoring its role in improving patient outcomes and supporting healthcare professionals.
Embrace the signal-to-noise ratio in your design process, and you’ll not only meet regulatory standards but also help set new benchmarks for usability in medical devices.
Contact us to learn more about signal-to-noise ratio and how we can assist your human factors needs.




